RFC 1349 redefined bits 3 and 6 (expanding for ToS bits) to reflect a desired type of service optimization. Table 1-5 shows the ToS field values that indicate service parameters to use for IP packets.
Table 1-5 ToS Field Values
| ToS Bits 3 to 6 | Description |
| 0000 | Normal service |
| 1000 | Minimize delay |
| 0100 | Maximize throughput |
| 0010 | Maximize reliability |
| 0001 | Minimize monetary cost |
In 1998, RFC 2474 redefined the ToS octet as the Differentiated Services (DS) field and further specified bits 0 through 5 as the Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) bits to support differentiated services. RFC 3168 (2001) updates RFC 2474, with the specification of an Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) field.
The DS field takes the form shown in Figure 1-2. The DS field provides more granular levels of packet classification by using 6 bits for packet marking. DS has 26 = 64 levels of classification, which is significantly higher than the eight levels of the IP precedence bits. These 64 levels are called codepoints, and they have been defined to be backward compatible with IP precedence values. RFCs 2474, 3246, and 3260 define three sets of PHBs: Class Selector (CS), Assured Forwarding (AF), and Expedited Forwarding (EF). The CS PHB set is for DSCP values that are compatible with IP precedence bits. The AF PHB set is used for queuing and congestion avoidance. The EF PHB set is used for premium service. The CS per-hop behaviors (PHB), in the form of xxx000, make it backward compatible with IP precedence.
A network designer uses DSCP to give priority to IP packets using Cisco routers. Routers should be configured to map these codepoints to PHBs with queuing or other bandwidth-management techniques. Table 1-6 compares DSCP and IP precedence values used to assign priority and apply policies to IP packets.
Table 1-6 DSCP and IP Precedence Values
| IP Precedence | Limitation | DSCP | |||
| Service Type | Decimal | Binary | Class | Decimal | Codepoint |
| Routine | 0 | 000 | Best effort | 0 | 000000 |
| Priority | 1 | 001 | Assured Forwarding (AF) Class 1 | 8 to 14 | 001xxx |
| Immediate | 2 | 010 | AF Class 2 | 16 to 22 | 010xxx |
| Flash | 3 | 011 | AF Class 3 | 24 to 30 | 011xxx |
| Flash override | 4 | 100 | AF Class 4 | 32 to 38 | 100xxx |
| Critical | 5 | 101 | Expedited Forwarding (EF) | 40 to 46 | 101xxx |
| Internetwork control | 6 | 110 | Control | 48 | 110xxx |
| Network control | 7 | 111 | Control | 56 | 111xxx |
RFC 2597 defines recommended values for AF codepoints with low, medium, and high packet-drop precedence. Table 1-7 shows the recommended AF codepoint values.
Table 1-7 DSCP AF Packet-Drop Precedence Values
| Precedence | AF Class 1 | AF Class 2 | AF Class 3 | AF Class 4 |
| Low drop precedence | 001010 | 010010 | 011010 | 100010 |
| Medium drop precedence | 001100 | 010100 | 011100 | 100100 |
| High drop precedence | 001110 | 010110 | 011110 | 100110 |
RFC 2598 defines the EF PHB for low loss, loss latency, and assured bandwidth types of traffic. This is considered a premium service. Traffic such as VoIP is classified as EF. The codepoint for EF is 101110, which corresponds to a DSCP value of 46.
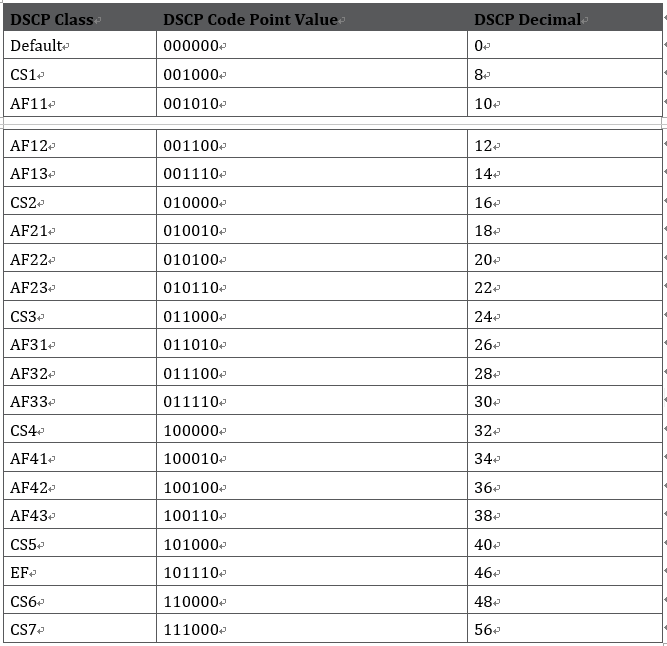
When you are configuring Cisco routers, some options are preconfigured and summarize the defined values for DSCP (see Table 1-8).
Table 1-8 IP DSCP Values